Unvented Attic Cold Climate

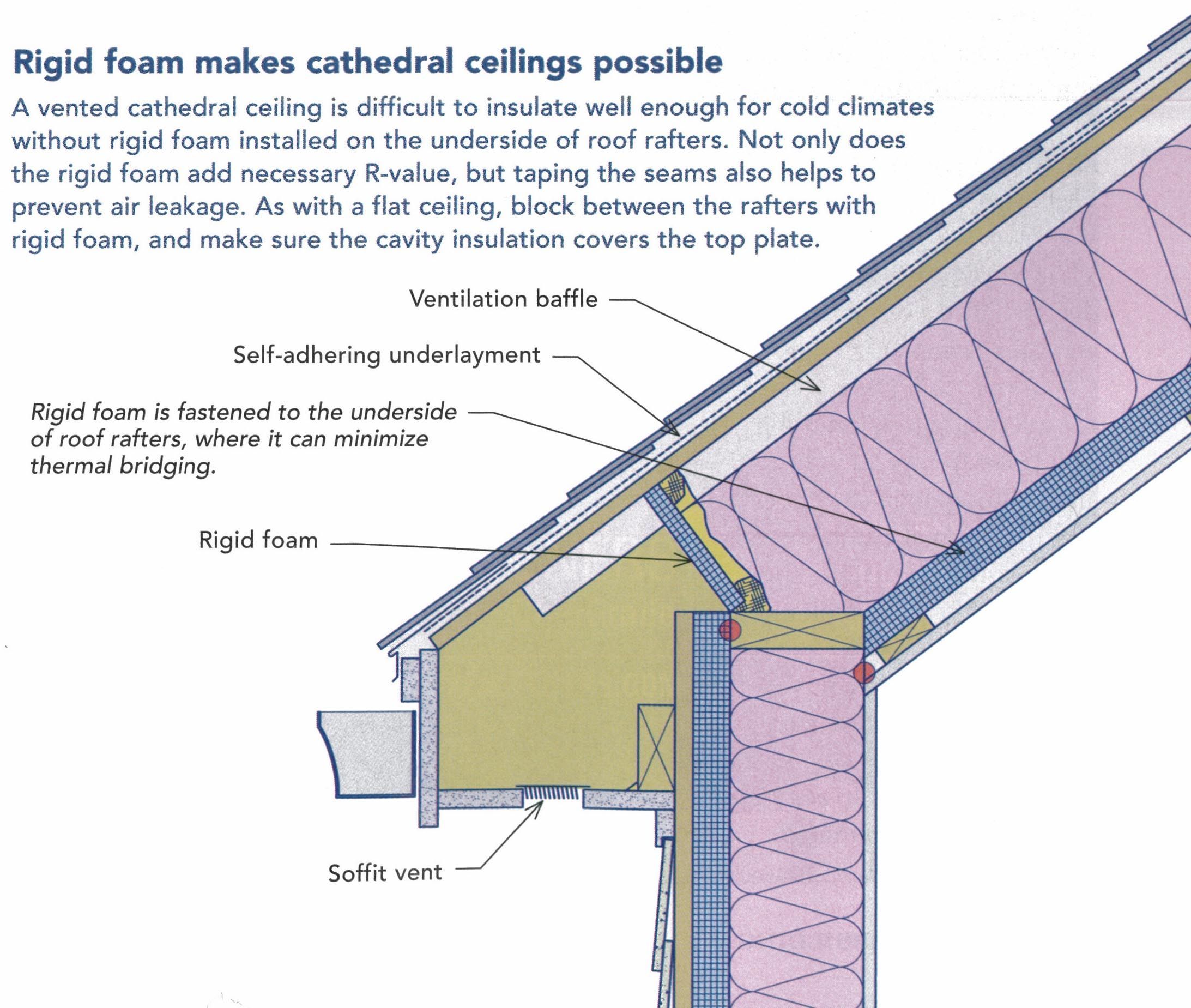
For example if an r 80 unvented cathedralized attic is to be constructed in a cold climate a minimum of r 40 50 should be air impermeable insulation installed and layered according to section r806 5 of the 2012 irc figure 4.
Unvented attic cold climate. Some spray foam manufactures have tested primer coating products that result in the formulation of a class ii vapor retarder directly on the surface of the open cell spray foam. Two acceptable methods for insulating an unvented attic assembly in all climates are as follows. Unvented attics have higher temperatures on the underside of the roof sheathing. Vented roofs serve a number of different purposes and their roles vary from climate to climate.
In cold climate locations with significant snowfalls ice dam formation on roofs is a real concern. Open cell spray foam can also be used to create an unvented attic in cold climate zones provided code requirements for a vapor retarder are followed. People usually vent attics in cold climates to prevent moisture accumulation in the roof sheathing and control ice dams. This is done by using what is referred to as air impermeable insulation such as rigid foam board or spray foam.
Air impermeable insulation typically spray foam installed to the underside of the roof sheathing. In any event a growing number of manufacturers are offering competitive warranties for roofing over unvented attic assemblies recognizing a significant marketing opportunity for their products. In cold climates moisture in roof assemblies typically comes from inside and the key to problems with moisture is the temperature of the roof sheathing.