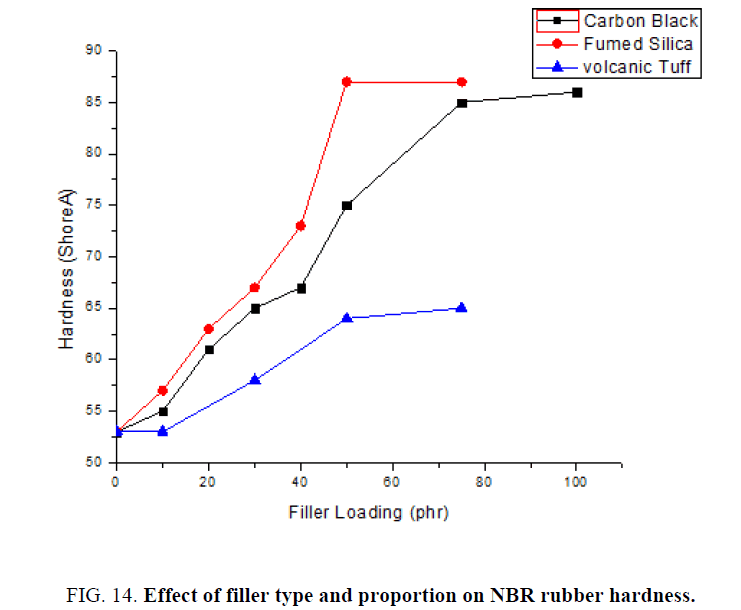
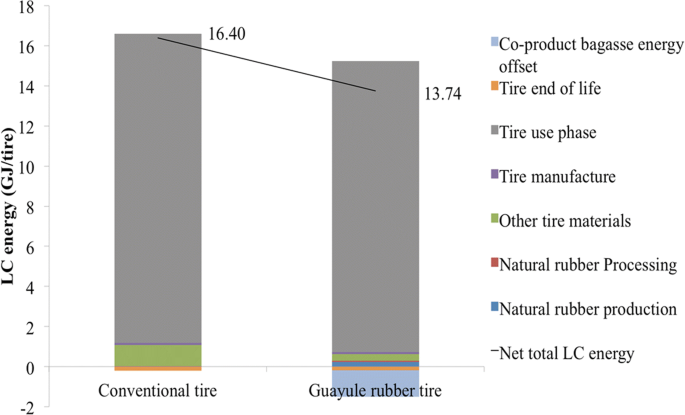
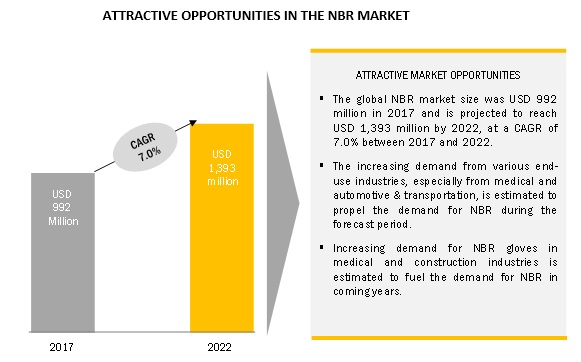
Specific Heat Capacity Of Natural Rubber

In some cases the molecular friction can cause the rubber to heat up to the point that either the metal to rubber bond fails or the rubber itself does.
Specific heat capacity of natural rubber. For conversion of units use the specific heat online unit converter. Some theoretical considerations on the transition phenomena at 200 k are included. The constant volume specific heat of natural rubber is calculated from the constant pressure specific heat which is measured experimentally and it is shown that the low temperature part is expressed by a combination of the debye and einstein formulas. The natural rubber specific heat capacity dependence on pressure was estimated on thermodynamic grounds on the basis of the values empirically determined from differential scanning calorimetry data in the temperature range of 70 to 50 c and by means of the tait equation of state in the pressure range of 0 1 240 mpa.
Material j kg k btu lbm f j kg c kj kg k aluminium 887 0 212 887 0 887 asphalt 915 0 21854 915 0 915 bone 440 0 105 440 0 44 boron 1106 0 264 1106 1 106 brass 920. See also tabulated values for gases food and foodstuff metals and semimetals common liquids and fluids and common solids as well as values of molar specific heat for common organic substances and inorganic substances. Below this table is an image version for offline viewing. Normally this can be counteracted by choosing a rubber compound with lower dynamic stiffness using a higher volume of rubber or applying special low damping or high elastic compounds.
The specific heat of some commonly used solids is given in the table below. The natural rubber specific heat capacity dependence on pressure was estimated on thermodynamic grounds on the basis of the values empirically determined from differential scanning calorimetry. The specific heat capacity of the compounds was also determined. Specific heat online unit converter.
The specific heat capacity of materials ranging from water to uranium has been listed below in alphabetical order.